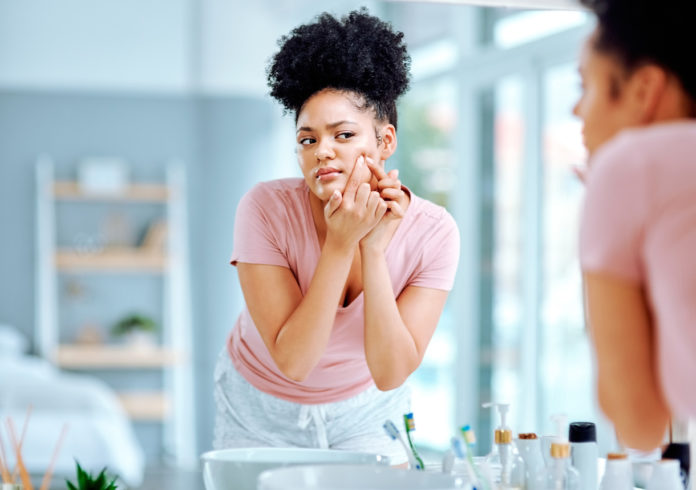
defining characteristics
disease development
Starts w/ occlusion of follicle and formation of microcomedone, leading to hyperkeratosis of the opening that blocks eggressive sebum. Cyst forms with sebaceous material, forming comedone. Follicular unit further expands, allowing growth of Propionibacterium acnes and inflammation that leads to follicular wall rupture
Inflammation mediated by bacteria intxn w/ TLR2 on monocytes
potential causes
Propionibacteria acnes (nl skin flora)
epidemiology
risk factors
labimaging
conventional treatment
Topical/oral antibiotics (reduce bacterial density and macrophage activation)
Retinoic acid (downregulates TLR2 expression on monocytes)
complications
Possible scarring