defining characteristics
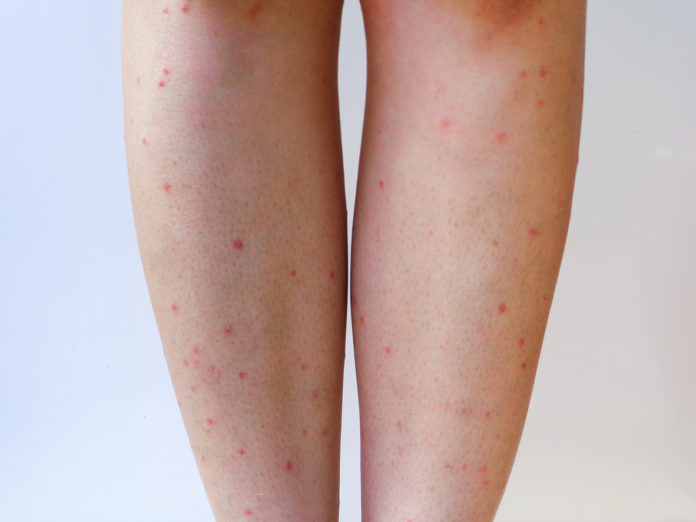
Itching, redness, erythematous papules; possible spongiosis and edema –> crusted vesicles;
Diaper dermatitis (irritant, also caused by Candida), poison ivy ACD – due to oleoresin in Rhus group of plants); nickel ACD neomycin ACD; formaldehyde ACD
disease development
Allergic – patient becomes sensitized from previous allergen exposure (no rash at first exposure); upon re-exposure to antigen, there is a delayed-hypersensitivity reaction
potential causes
Allergic – allergy response (poison ivy, does not occur in everybody)
epidemiology
risk factors
labimaging
Patch testing
conventional treatment
Avoid irritant/allergen; wash immediately after exposure; calomine to soothe/dry out (AVOID sensitizers like topical benadryl/Caladryl); topical corticosteroid