defining characteristics
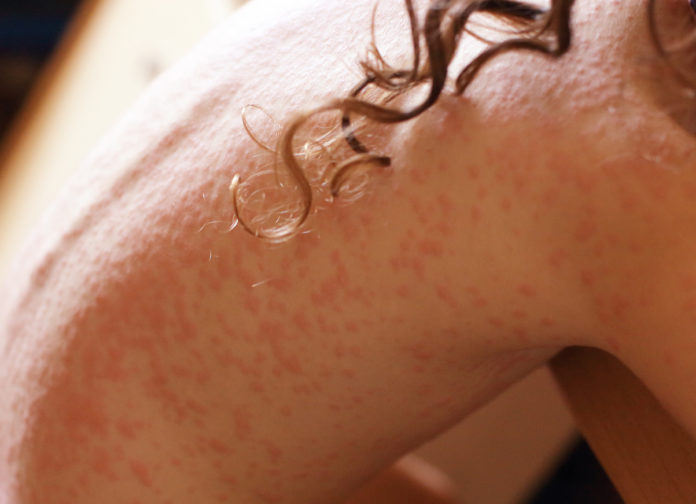
PRURITIC, thread like linear burrows produced by the tunneling of the mite; can have erythematous papules; commonly seen on wrists, genitals, waistline, axilla, web spaces
disease development
Eruption caused by tunneling of mite in stratum corneum that causes delayed type IV hypersensitivity response and diffuse pruritic eruption after 4-8 weeks
Transmitted via skin-skin contact or contact with fomites
potential causes
Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis
epidemiology
risk factors
Nursing home residents Children
Hospitals
Close contact areas
labimaging
Histology? Mites (ovals) in stratum corneum
Mineral oil prep? Mites with oval gray eggs and fecal pellets
conventional treatment
Topical creams (scabicides)
treatment of fomites and close contacts
can use oral anti-parasitic if severe (ivermectin)
complications
Rare (psychological burden?)