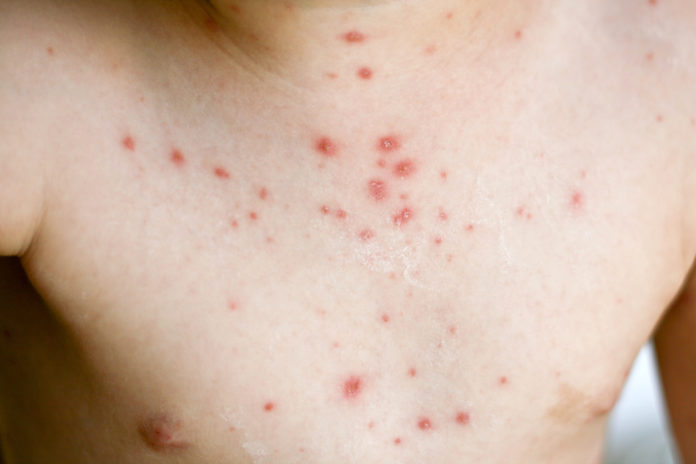
defining characteristics
PAINFUL, DERMATOMAL vesicles, crusted papules,
erosions often in unilateral fashion
disease development
VZV goes latent after active infection/vaccination in the ganglia until risk factors cause reactivation of varicella zoster virus
NOT contagious (represents reactivation state) but patients with varicella zoster can transmit chicken pox to those who have never had it
potential causes
Varicella zoster virus
epidemiology
Lifetime risk of 10-20%
risk factors
Advancing age immunosuppression Stress!
labimaging
Clinical Tzanck prep
DFA (distinguish HSV from VZV) Viral Cx
Bx (rare)
conventional treatment
ORAL ANTI-VIRALS ASAP!! (w/I
first 48-72h)
complications
POST-HERPETIC NEURALGIA
dissemination
transmission of varicella (chicken pox)
prevention
Prevention with immunization w/ zoster in people > 50y.o.